 |
Huawei Chairman Liang Hua speaks at the Tech & Sustainability: Everyone’s Included forum on July 8. (Huawei Technologies) |
Huawei Technologies‘ low-carbon projects across the world and its climate-related track record are now in the spotlight, amid growing regulatory hurdles and customer demand regarding green technologies in South Korea.
Introducing its technologies to promote clean energy at a recent press conference held in Seoul, Karl Song, vice president of Huawei’s corporate communications department, said the company is ready to play a role in empowering its Korean partners‘ pursuit of low-carbon missions.
“Empowering a low-carbon ICT industry is one of our top priorities. We believe that the ICT industry should first reduce its own power consumption and emissions to support green development,” Song told reporters in Seoul.
“We aim to increase the energy efficiency of all of our products by 2.7 times by 2025, and that is just the beginning,” Song said.
Huawei’s green technological solution includes fifth-generational active antenna units, which enable a cut in power consumption by 30 percent while providing the same level of coverage, and smart on-demand heating solutions that reduce energy use by an average of 12 percent. Its on-demand heating solution has already been adopted in China‘s northeastern city Harbin.
In terms of renewable energy solutions, Huawei has developed an eco-friendly smart photovoltaic solution for solar energy across desert land in Qinghai, China, by working with partners, Song said. The solution has not only generated renewable energy, but also supported animal husbandry, as well as increased soil quality and restored vegetation.
Huawei green technology has evolved amid growing global need for low-carbon electricity generation and electric energy consumption. The current information and communication technologies have often been held responsible for carbon footprints with power usage and raw material selection, among other factors.
So too, South Korean tech firms have been pushed to minimize their carbon footprint and accelerate the shift to renewable energy sources and smart tech solutions.
Behind the movement is growing regulatory pressure.
Under its net-zero goal declared in 2020, South Korea expects a significant cut in carbon emissions from 2018’s 727.6 million metric tons to 436.6 million metric tons in 2030.
To reach its goal, the government has been urging manufacturers to reduce carbon emissions by 14.5 percent from the 2018 record of 260.5 million metric tons to 222.6 million metric tons in 2030.
 |
Fang Liangzhou, vice president and chief marketing officer of Huawei Digital Power, delivers a speech virtually at COP26. (Huawei Technologies) |
South Korea’s pursuit of low-carbon emissions is in line with Huawei‘s technological advancement, according to officials at the company.
Huawei’s Digital Power Solutions is one example. Its solutions are used across smart solar panels, storage and artificial intelligence-run technologies to reduce power consumption. Deployed in more than 170 countries and regions, Huawei has been providing off-grid fuel-removal power supply solutions, prefab technologies to build simplified data centers and charging infrastructure to help businesses achieve low-carbon outcomes.
To date, these solutions have generated 443.5 billion kilowatt-hours of electricity from renewable sources, and saved 13.6 billion kilowatt-hours of electricity, reducing 210 million tons in carbon dioxide emissions -- equivalent to planting 290 million trees, as of September this year, Huawei said.
More projects by Huawei‘s Digital Power Solutions are underway to reduce carbon footprint.
For example, Huawei is taking part in what could give birth to a city fully powered by clean energy and storage. Called Red Sea Energy Storage Project, the project in Saudi Arabia aims to build the planned city in Neom, Tabuk province, in Saudi Arabia, which will use the 400-megawatt photovoltaic energy and 1.3-gigawatt-hour energy storage system.
The solution was introduced in a session of COP26 in November, as an example to integrate digital and power electronics technologies to help industries save energy and reduce emissions.
“Technological innovation will play a central role in tackling climate change and achieving decarbonization goals,” said Fang Liangzhou, vice president and chief marketing officer of Huawei Digital Power.
“We focus on converged innovation of technologies to accelerate the digitalization of energy and enable various industries to reach the next level. We aim to accelerate clean power generation, build green transportation, sites and data centers, and work with industry partners to build a low-carbon smart society.”
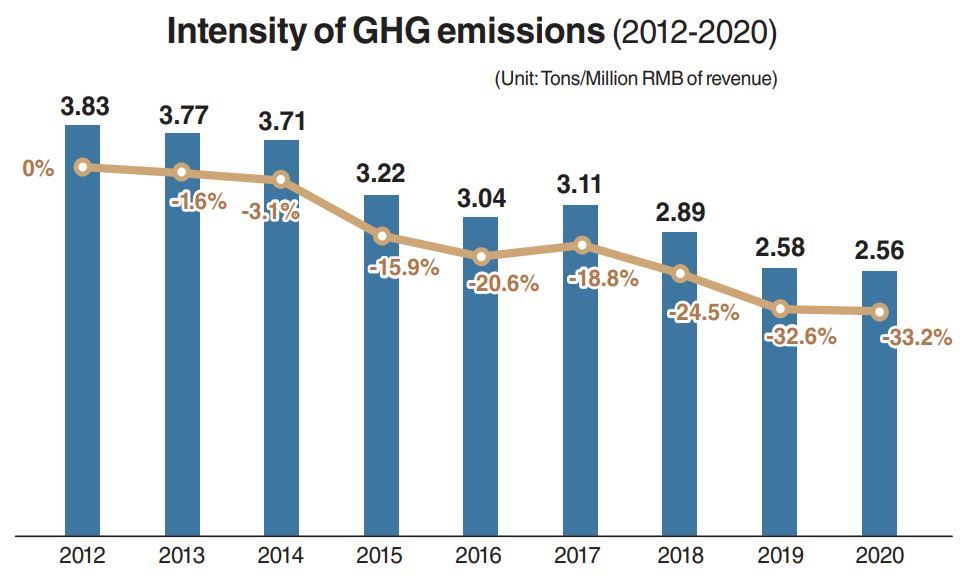
Huawei has a history of achieving carbon emission targets, as suggested in its 2020 Sustainability Report released in July.
In 2020, Huawei‘s carbon emissions per 1 million yuan ($157,000) of sales revenue averaged 2.56 tons, representing a 33.2 percent decrease compared to 2012. This beat its low-carbon target set in 2016 -- a cut by 30 percent in eight years.
Along with this, Huawei has achieved its goals of purchasing at least 1.55 billion kilowatt-hours of electricity powered by clean energy sources, saving more than 10 million kilowatt-hours of energy in administrative services, reducing ICT waste sent to landfills to 1.5 percent or lower out of the total waste disposed of, exhausting zero water or gas emissions in violation of regulations and encouraging more than 60 of its top 100 suppliers to set a carbon emissions reduction target, according to the report.
In 2020, Huawei was recognized as on the Climate A List by nonprofit organization CDP, which measured over 5,800 companies’ environmental and climate actions.
“An intelligent world should also be a green world. Advances in technology can help us better understand and protect nature, mitigating the impact of human activity on the planet. We believe that technology can work in harmony with nature and help make this world a better place,” Huawei Chairman Liang Hua noted in the report.
Environmental protection is one of the key themes suggested in the report, along with digital inclusion, security and trustworthiness, and a healthy and harmonious ecosystem.
 |
Cover of Huawei’s 2020 Sustainability Report (Huawei Technologies) |








![[Exclusive] Hyundai Mobis eyes closer ties with BYD](http://res.heraldm.com/phpwas/restmb_idxmake.php?idx=644&simg=/content/image/2024/11/25/20241125050044_0.jpg)
![[Herald Review] 'Gangnam B-Side' combines social realism with masterful suspense, performance](http://res.heraldm.com/phpwas/restmb_idxmake.php?idx=644&simg=/content/image/2024/11/25/20241125050072_0.jpg)

