For Korean trade union members, spring is a tough season as they traditionally undergo collective bargaining with company management over annual wages and other working conditions. The collective bargaining period often turned sour and violent in the past decades.
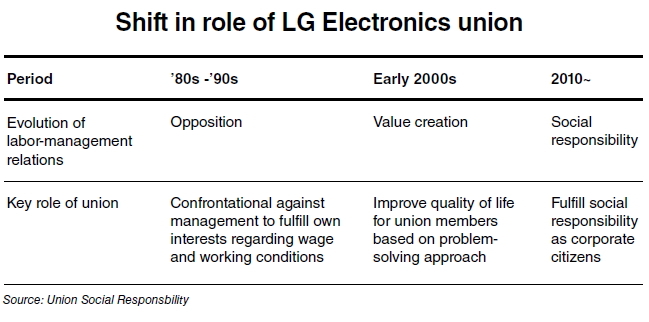
Winds of change arrived in the nation’s industrial relations in the early 2000s when labor relations evolved into cooperative or value-creating ones, following the confrontational period in the 1980s and 1990s.
“LG Electronics started searching for a different model in its industrial relations from the early 2000s, considering setbacks from confrontational relations between labor and management are a key risk to the company’s future,’’ Kim Young-kee, who served as LGE’s chief human resource officer between 2000 and 2007, said in an interview with The Korea Herald. Kim is currently responsible for corporate social responsibility at LG Corp., the holding company of LG Group, as an executive vice president.
 |
Kim Young-kee |
Unlike other conglomerates, representatives from management and labor unions took field trips to the U.S. and European countries together to research model cases for industrial relations. LG Electronics, one of the nation’s flagship corporate brands, finally launched advanced labor relations beyond cooperative ones in January 2010, called the LGE Union Social Responsibility Charter.
“USR refers to a socially responsible union, stressing bigger roles and responsibilities of the union as a member of society,” Kim said, adding that USR is meaningful in that it is a more advanced labor-management relations model in Korea than the prevalent cooperative model based on mutual trust between labor and management.
The new model started with the enhanced definition of quality of life for union members, the top objective of the union. Quality of life is not limited to wages and working conditions in the sophisticated modern society and it is closely tied to external issues beyond the worksite such as human rights, regional society and even the global environment.
“A socially responsible union cares about its diversified stakeholders in and out of the company,” Kim said.
The LGE union voluntarily develops detailed annual three-pillar action plans to carry out its bigger role for social contribution activities in the economic, social and environmental fields, and implements and evaluates them. To evaluate the USR’s impact, Kim conducted a survey of 800 LGE union members in October 2010 on their participation in USR activities and their commitment to the company.
“The survey found a correlation between USR activities and the commitment of union members to the company and their satisfaction at work, which are key indicators of organizational performance,” Kim said.
Kim, who attained a Ph.D. in USR and organizational performance from the Seoul School of Integrated Science & Technologies in 2011, recently published an English-language book titled “Union Social Responsibility” to present the positive effect of a socially responsible union to the company with Bae Sang-ho, head of LG Electronics’ labor union.
“Most Korean companies still stay at confrontational or cooperative labor relations, but the union and management should pay attention to the socially responsible union model for a better life of union members and corporate performance,” Kim said.
USR is spreading into other affiliates of LG Group such as LG Display and LG Innotek.
In addition, LG Group has encouraged its overseas branches to adopt USR at their worksites since last year.
By Seo Jee-yeon (
jyseo@heraldcorp.com)






![[Exclusive] Hyundai Mobis eyes closer ties with BYD](http://res.heraldm.com/phpwas/restmb_idxmake.php?idx=644&simg=/content/image/2024/11/25/20241125050044_0.jpg)
![[Herald Review] 'Gangnam B-Side' combines social realism with masterful suspense, performance](http://res.heraldm.com/phpwas/restmb_idxmake.php?idx=644&simg=/content/image/2024/11/25/20241125050072_0.jpg)

