In this second installment of our series on automotive cybersecurity, we delve deeper into the strategic approach to regulatory compliance, focusing on Vehicle Type Approval (VTA) and its challenges.
Until five years ago, carmakers were hesitant to introduce cybersecurity measures in vehicles despite being aware of their necessity due to cost issues.
However, when the European Union introduced cybersecurity regulations in 2022, it became virtually impossible to enter the European market without meeting the new standards. The change has made cybersecurity an essential element to ensure the survival of carmakers.
The advancements in vehicle software, diversification of vehicles’ functions and increase in communication have made software-defined vehicles (SDVs) a hot topic for the car industry, and cybersecurity is the final element in building SDVs.
The fact that UNECE WP.29 adopted UN Regulation No. 155 (UN R155) in June 2020 to lay the foundations for the cybersecurity ecosystem is widely known.
1. CSMS and ISO/SAE 21434
The core of UN R155 is that carmakers need to obtain a cybersecurity management system (CSMS) and vehicle type approval. CSMS refers to the process and management system for protecting vehicles from cyberattacks and managing cybersecurity risks. ISO/SAE 21434 is the international engineering standard for vehicle cybersecurity that defines the cybersecurity policies and processes throughout all phases of a vehicle’s development, production and postproduction, and sets the standards for CSMS.
The UN R155 outlines its aims, while the ISO/SAE 21434 provides the requirements and details about assessment standards. In other words, ISO/SAE 21434 is essential to properly implement CSMS.
2. Understanding VTA's purpose and requirements
As previously explained, the Cyber Security Management System is integral to protecting road vehicles against cyberthreats. The VTA process begins with the technical service (TS) evaluating the automaker's technical documentation and conducting initial vehicle tests. Following TS approval, the approval authority (AA) issues a final CSMS certificate following its own review. VTA ensures each vehicle adheres to the prescribed cybersecurity standards, with both TS and AA validating the implementation.
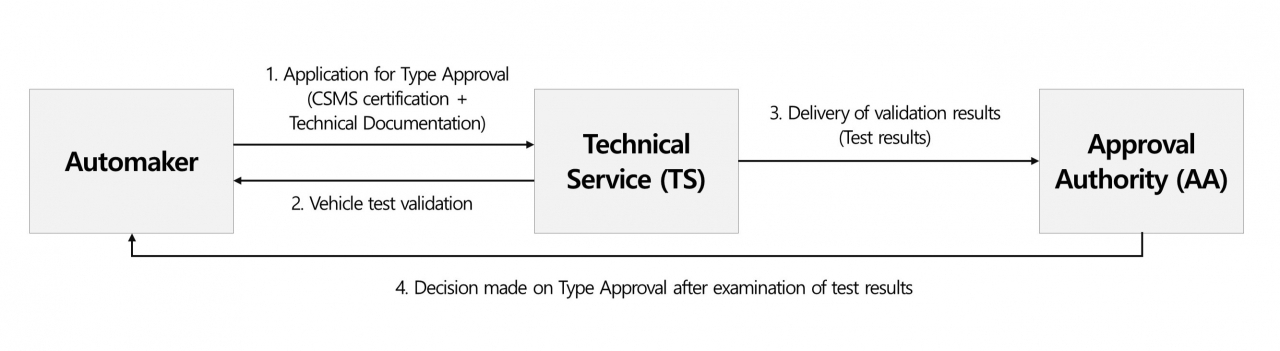 |
UN R155's cybersecurity certification process (FESCARO) |
VTA necessitates comprehensive risk assessment, effective cybersecurity measures, and thorough validation testing. This includes identifying risks to road vehicles and determining the adequacy of the risk management strategy, which could involve removal, improvement, avoidance, or acceptance of risks. The specifics of these cybersecurity measures are detailed in UN Regulation No. 155 (UN R155) Articles 5 ("approval") and 7 ("specifications"), with the specific testing protocols outlined in ISO/SAE 21434.
3. Conducting cybersecurity testing for VTA
The ISO/SAE 21434 outlines a four-step validation process for road vehicles: functional testing, vulnerability scanning, fuzzing testing and penetration testing. Each step has a specific focus, from verifying the operation of cybersecurity elements to actively simulating attacks to identify potential vulnerabilities. The type of testing required for each Electronic Control Unit (ECU) is determined by its Cybersecurity Assurance Level as specified in Annex E of ISO/SAE 21434, shown in the table below:
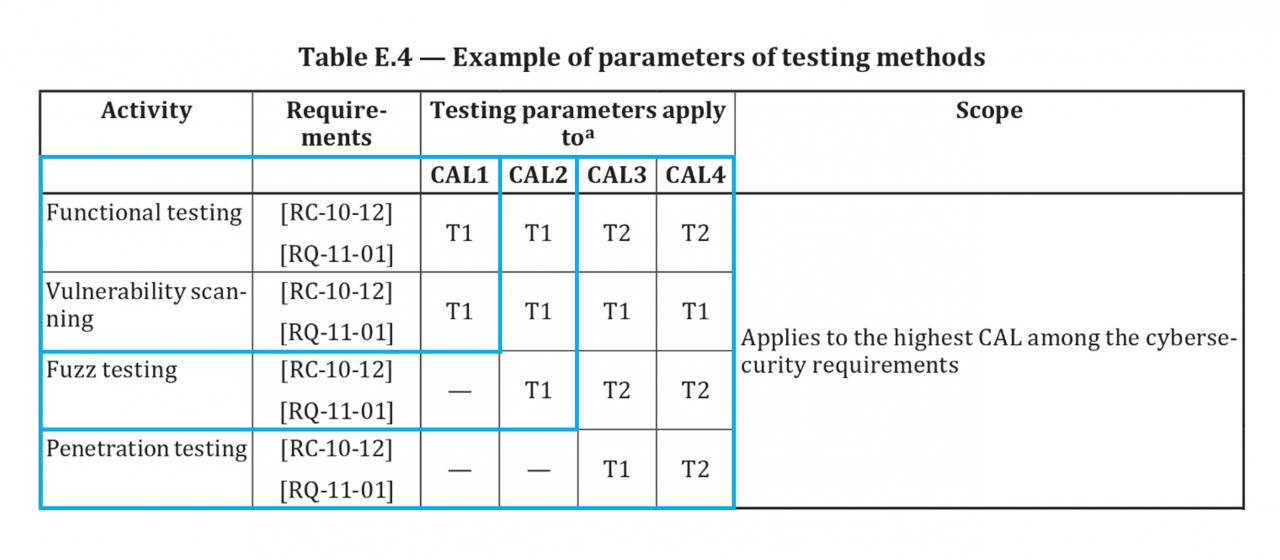 |
Cybersecurity Assurance Level assigned to each Electronic Control Unit (ISO/SAE 21434, Annex E) |
4. Key insights of VTA and FESCARO's expertise
Ensuring the correct setup and application of cybersecurity measures is crucial for the safety of ECUs and vehicles. FESCARO emphasizes a comprehensive approach, integrating threat analysis and risk assessment (TARA), robust cybersecurity solutions, rigorous testing, and effective cybersecurity control management.
FESCARO’s success story with an internationally renowned automaker highlights the importance of choosing a competent cybersecurity partner. During a recent penetration test for a world-renowned automaker, we identified a critical issue in an electric vehicle's powertrain system -- when tested in motion, the drivetrain failed and the gas pedal became unresponsive. Our team of experts swiftly reported this issue to the automaker, and after a thorough review, we successfully applied a cybersecurity patch to resolve the problem.
5. Essential takeaway from VTA experience
The essence of VTA lies in thorough verification and validation of cybersecurity measures. This process must be both rigorous and continuous in order to prevent unforeseen cybersecurity events.
FESCARO's three-year journey underscores the importance of exhaustive testing and consistent technology application. Real-vehicle testing is critical for comprehensive validation as stipulated in UN R155. Our strategy for successful VTA includes meticulous TARA documentation, extensive ECU testing, real-life vehicle trials, comprehensive VTA evaluation checklists, and seamless integration of cybersecurity testing with IT infrastructure.
In our next article, we will explore the final step of automotive cybersecurity certification: SUMS certification, and discuss the prerequisites for achieving it.
[Ku Seong-seo, Fescaro head of global business sales at fescaro.com ]
Fescaro is a vehicle cybersecurity specialist that has gone through all major certification processes (CSMS, ISO/SAE 21434, VTA, SUMS). It is the only company in Korea to have obtained what is referred to in the field as the "grand slam of vehicle cybersecurity certification consulting.” - Ed






![[Weekender] Korea's traditional sauce culture gains global recognition](http://res.heraldm.com/phpwas/restmb_idxmake.php?idx=644&simg=/content/image/2024/11/21/20241121050153_0.jpg)
